Array Computing
Array computing is the foundation of statistical, mathematical, scientific computing in various contemporary data science and analytics applications such as data visualization, digital signal processing, image processing, bioinformatics, machine learning, AI, and several others.
Large scale data manipulation and transformation depends on efficient, high-performance array computing. The language of choice for data analytics, machine learning, and productive numerical computing is Python.
Numerical Python or NumPy is its de-facto standard Python programming language library that supports large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, and comes with a vast collection of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays.
Since the launch of NumPy in 2006, Pandas appeared on the landscape in 2008, and it was not until a couple of years ago that several array computing libraries showed up in succession, crowding the array computing landscape. Many of these newer libraries mimic NumPy-like features and capabilities, and pack newer algorithms and features geared towards machine learning and artificial intelligence applications.
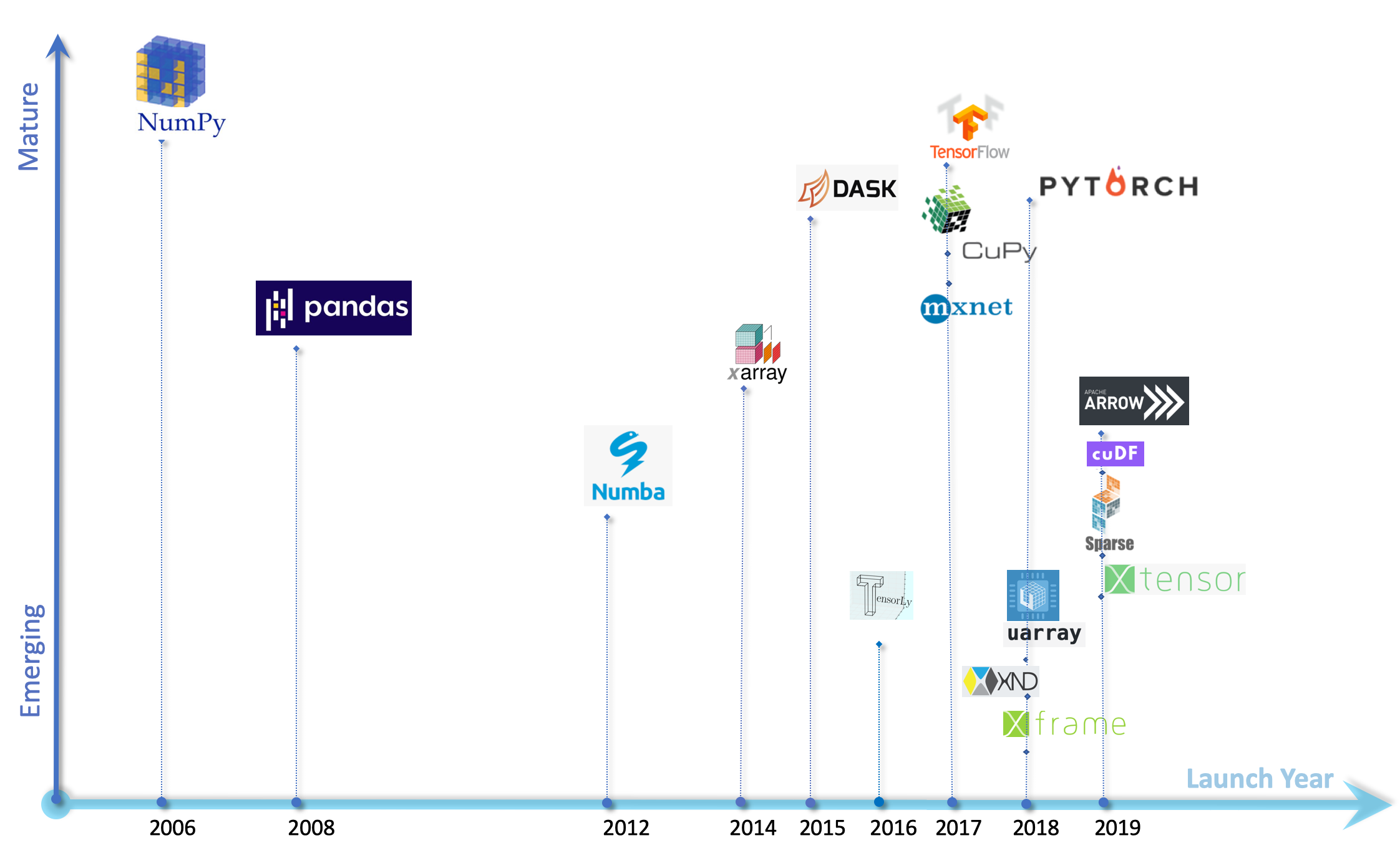
Array computing is based on arrays data structures. Arrays are used to organize vast amounts of data such that a related set of values can be easily sorted, searched, mathematically manipulated, and transformed easily and quickly.
Array computing is unique as it involves operating on the data array at once. What this means is that any array operation applies to an entire set of values in one shot. This vectorized approach provides speed and simplicity by enabling programmers to code and operate on aggregates of data, without having to use loops of individual scalar operations.