numpy.random.RandomState.logseries¶
-
RandomState.logseries(p, size=None)¶ Draw samples from a logarithmic series distribution.
Samples are drawn from a log series distribution with specified shape parameter, 0 <
p< 1.Parameters: p : float or array_like of floats
Shape parameter for the distribution. Must be in the range (0, 1).
size : int or tuple of ints, optional
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g.,
(m, n, k), thenm * n * ksamples are drawn. If size isNone(default), a single value is returned ifpis a scalar. Otherwise,np.array(p).sizesamples are drawn.Returns: out : ndarray or scalar
Drawn samples from the parameterized logarithmic series distribution.
See also
scipy.stats.logser- probability density function, distribution or cumulative density function, etc.
Notes
The probability density for the Log Series distribution is
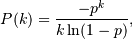
where p = probability.
The log series distribution is frequently used to represent species richness and occurrence, first proposed by Fisher, Corbet, and Williams in 1943 [2]. It may also be used to model the numbers of occupants seen in cars [3].
References
[R171] Buzas, Martin A.; Culver, Stephen J., Understanding regional species diversity through the log series distribution of occurrences: BIODIVERSITY RESEARCH Diversity & Distributions, Volume 5, Number 5, September 1999 , pp. 187-195(9). [R172] Fisher, R.A,, A.S. Corbet, and C.B. Williams. 1943. The relation between the number of species and the number of individuals in a random sample of an animal population. Journal of Animal Ecology, 12:42-58. [R173] D. J. Hand, F. Daly, D. Lunn, E. Ostrowski, A Handbook of Small Data Sets, CRC Press, 1994. [R174] Wikipedia, “Logarithmic distribution”, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logarithmic_distribution Examples
Draw samples from the distribution:
>>> a = .6 >>> s = np.random.logseries(a, 10000) >>> count, bins, ignored = plt.hist(s)
# plot against distribution
>>> def logseries(k, p): ... return -p**k/(k*log(1-p)) >>> plt.plot(bins, logseries(bins, a)*count.max()/ logseries(bins, a).max(), 'r') >>> plt.show()