numpy.random.sample¶
-
numpy.random.sample(size=None)¶ Return random floats in the half-open interval [0.0, 1.0).
Results are from the “continuous uniform” distribution over the stated interval. To sample
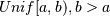 multiply
the output of
multiply
the output of random_sampleby (b-a) and add a:(b - a) * random_sample() + a
Parameters: size : int or tuple of ints, optional
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g.,
(m, n, k), thenm * n * ksamples are drawn. Default is None, in which case a single value is returned.Returns: out : float or ndarray of floats
Array of random floats of shape size (unless
size=None, in which case a single float is returned).Examples
>>> np.random.random_sample() 0.47108547995356098 >>> type(np.random.random_sample()) <type 'float'> >>> np.random.random_sample((5,)) array([ 0.30220482, 0.86820401, 0.1654503 , 0.11659149, 0.54323428])
Three-by-two array of random numbers from [-5, 0):
>>> 5 * np.random.random_sample((3, 2)) - 5 array([[-3.99149989, -0.52338984], [-2.99091858, -0.79479508], [-1.23204345, -1.75224494]])