numpy.linspace¶
-
numpy.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None, axis=0)[source]¶ Return evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval.
Returns num evenly spaced samples, calculated over the interval [start, stop].
The endpoint of the interval can optionally be excluded.
Changed in version 1.16.0: Non-scalar start and stop are now supported.
- Parameters
- startarray_like
The starting value of the sequence.
- stoparray_like
The end value of the sequence, unless endpoint is set to False. In that case, the sequence consists of all but the last of
num + 1evenly spaced samples, so that stop is excluded. Note that the step size changes when endpoint is False.- numint, optional
Number of samples to generate. Default is 50. Must be non-negative.
- endpointbool, optional
If True, stop is the last sample. Otherwise, it is not included. Default is True.
- retstepbool, optional
If True, return (samples, step), where step is the spacing between samples.
- dtypedtype, optional
The type of the output array. If
dtypeis not given, infer the data type from the other input arguments.New in version 1.9.0.
- axisint, optional
The axis in the result to store the samples. Relevant only if start or stop are array-like. By default (0), the samples will be along a new axis inserted at the beginning. Use -1 to get an axis at the end.
New in version 1.16.0.
- Returns
- samplesndarray
There are num equally spaced samples in the closed interval
[start, stop]or the half-open interval[start, stop)(depending on whether endpoint is True or False).- stepfloat, optional
Only returned if retstep is True
Size of spacing between samples.
See also
Examples
>>> np.linspace(2.0, 3.0, num=5) array([2. , 2.25, 2.5 , 2.75, 3. ]) >>> np.linspace(2.0, 3.0, num=5, endpoint=False) array([2. , 2.2, 2.4, 2.6, 2.8]) >>> np.linspace(2.0, 3.0, num=5, retstep=True) (array([2. , 2.25, 2.5 , 2.75, 3. ]), 0.25)
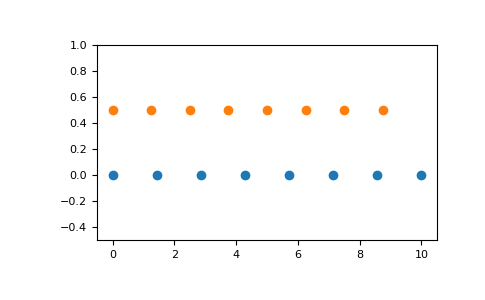
Graphical illustration:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> N = 8 >>> y = np.zeros(N) >>> x1 = np.linspace(0, 10, N, endpoint=True) >>> x2 = np.linspace(0, 10, N, endpoint=False) >>> plt.plot(x1, y, 'o') [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>] >>> plt.plot(x2, y + 0.5, 'o') [<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>] >>> plt.ylim([-0.5, 1]) (-0.5, 1) >>> plt.show()