numpy.unwrap#
- numpy.unwrap(p, discont=None, axis=-1, *, period=6.283185307179586)[source]#
Unwrap by taking the complement of large deltas with respect to the period.
This unwraps a signal p by changing elements which have an absolute difference from their predecessor of more than
max(discont, period/2)to their period-complementary values.For the default case where period is \(2\pi\) and discont is \(\pi\), this unwraps a radian phase p such that adjacent differences are never greater than \(\pi\) by adding \(2k\pi\) for some integer \(k\).
- Parameters:
- parray_like
Input array.
- discontfloat, optional
Maximum discontinuity between values, default is
period/2. Values belowperiod/2are treated as if they wereperiod/2. To have an effect different from the default, discont should be larger thanperiod/2.- axisint, optional
Axis along which unwrap will operate, default is the last axis.
- periodfloat, optional
Size of the range over which the input wraps. By default, it is
2 pi.New in version 1.21.0.
- Returns:
- outndarray
Output array.
Notes
If the discontinuity in p is smaller than
period/2, but larger than discont, no unwrapping is done because taking the complement would only make the discontinuity larger.Examples
>>> import numpy as np
>>> phase = np.linspace(0, np.pi, num=5) >>> phase[3:] += np.pi >>> phase array([ 0. , 0.78539816, 1.57079633, 5.49778714, 6.28318531]) # may vary >>> np.unwrap(phase) array([ 0. , 0.78539816, 1.57079633, -0.78539816, 0. ]) # may vary >>> np.unwrap([0, 1, 2, -1, 0], period=4) array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) >>> np.unwrap([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1, 2, 3], period=6) array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) >>> np.unwrap([2, 3, 4, 5, 2, 3, 4, 5], period=4) array([2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) >>> phase_deg = np.mod(np.linspace(0 ,720, 19), 360) - 180 >>> np.unwrap(phase_deg, period=360) array([-180., -140., -100., -60., -20., 20., 60., 100., 140., 180., 220., 260., 300., 340., 380., 420., 460., 500., 540.])
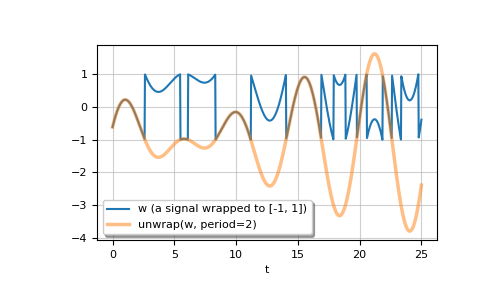
This example plots the unwrapping of the wrapped input signal w. First generate w, then apply
unwrapto get u.>>> t = np.linspace(0, 25, 801) >>> w = np.mod(1.5 * np.sin(1.1 * t + 0.26) * (1 - t / 6 + (t / 23) ** 3), 2.0) - 1 >>> u = np.unwrap(w, period=2.0)
Plot w and u.
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> plt.plot(t, w, label='w (a signal wrapped to [-1, 1])') >>> plt.plot(t, u, linewidth=2.5, alpha=0.5, label='unwrap(w, period=2)') >>> plt.xlabel('t') >>> plt.grid(alpha=0.6) >>> plt.legend(framealpha=1, shadow=True) >>> plt.show()