numpy.random.Generator.zipf#
method
- random.Generator.zipf(a, size=None)#
Draw samples from a Zipf distribution.
Samples are drawn from a Zipf distribution with specified parameter a > 1.
The Zipf distribution (also known as the zeta distribution) is a discrete probability distribution that satisfies Zipf’s law: the frequency of an item is inversely proportional to its rank in a frequency table.
- Parameters:
- afloat or array_like of floats
Distribution parameter. Must be greater than 1.
- sizeint or tuple of ints, optional
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g.,
(m, n, k), thenm * n * ksamples are drawn. If size isNone(default), a single value is returned ifais a scalar. Otherwise,np.array(a).sizesamples are drawn.
- Returns:
- outndarray or scalar
Drawn samples from the parameterized Zipf distribution.
See also
scipy.stats.zipfprobability density function, distribution, or cumulative density function, etc.
Notes
The probability mass function (PMF) for the Zipf distribution is
\[p(k) = \frac{k^{-a}}{\zeta(a)},\]for integers \(k \geq 1\), where \(\zeta\) is the Riemann Zeta function.
It is named for the American linguist George Kingsley Zipf, who noted that the frequency of any word in a sample of a language is inversely proportional to its rank in the frequency table.
References
[1]Zipf, G. K., “Selected Studies of the Principle of Relative Frequency in Language,” Cambridge, MA: Harvard Univ. Press, 1932.
Examples
Draw samples from the distribution:
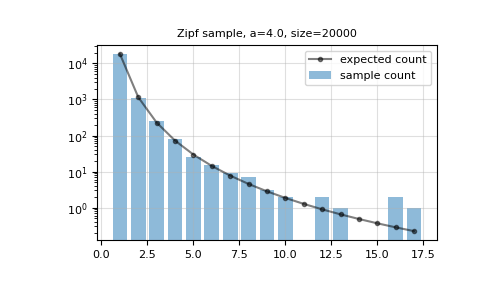
>>> a = 4.0 >>> n = 20000 >>> rng = np.random.default_rng() >>> s = rng.zipf(a, size=n)
Display the histogram of the samples, along with the expected histogram based on the probability density function:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> from scipy.special import zeta
bincountprovides a fast histogram for small integers.>>> count = np.bincount(s) >>> k = np.arange(1, s.max() + 1)
>>> plt.bar(k, count[1:], alpha=0.5, label='sample count') >>> plt.plot(k, n*(k**-a)/zeta(a), 'k.-', alpha=0.5, ... label='expected count') >>> plt.semilogy() >>> plt.grid(alpha=0.4) >>> plt.legend() >>> plt.title(f'Zipf sample, a={a}, size={n}') >>> plt.show()